Food & Drink
What 95% of Dieters Don’t Know About Food Marketing Is Mind-Blowing
Discover the shocking psychology behind food myths and how billion-dollar marketing tricks manipulate your nutrition beliefs. The truth will surprise you.
Published
2 weeks agoon

What if everything you believed about nutrition was carefully engineered by marketers who understand your brain better than you do? A staggering 95% of fad diets fail, yet millions continue falling for the same food myths year after year. The reason isn’t willpower—it’s a sophisticated psychological manipulation that turns marketing claims into deeply held beliefs about what’s healthy.
The Psychology Behind Our Food Beliefs
Our brains are wired to make quick decisions about food based on survival instincts that served our ancestors well but leave us vulnerable to modern marketing tactics. The food myths psychology at work here involves several cognitive biases that marketers exploit ruthlessly.
The Halo Effect in Food Marketing
When a product is labeled “low-fat,” “organic,” or “natural,” our brains automatically assume it’s healthier across all dimensions. This halo effect is so powerful that Harvard-trained oncologists report seeing patients who believe processed low-fat foods are superior to whole, natural alternatives.
The psychological mechanism works because:
- We process information faster using mental shortcuts (heuristics)
- Health claims trigger our desire for self-improvement
- Fear-based marketing activates our loss-aversion bias
- Social proof makes us follow perceived health trends
The Low-Fat Deception That Backfired
Perhaps no nutrition myth demonstrates the power of marketing psychology better than the low-fat craze that dominated American food culture for decades. Despite mounting scientific evidence, the myth persists—and it’s actually making us less healthy.
The Childhood Obesity Paradox
Studies consistently show that children who consume whole-fat dairy have lower odds of overweight and obesity than those consuming low-fat versions. This isn’t just correlation—the mechanism involves how fats affect satiety hormones and nutrient absorption.
A comprehensive analysis published in NZ Herald reveals that the low-fat movement created a perfect storm:
- Removing fat from foods required adding sugar and artificial ingredients
- Low-fat products triggered greater hunger and overeating
- Essential fat-soluble vitamins became harder to absorb
- Marketing convinced parents that “low-fat” meant “healthy for kids”
The psychology here is crucial: once we’re told something is healthier, we ignore contradicting evidence and even our own body’s signals.
Why 95% of Diets Are Designed to Fail
The fad diet industry has perfected a psychological trap that keeps customers coming back. The 95% failure rate isn’t a bug—it’s a feature that generates repeat business worth billions.
The Metabolic Sabotage Cycle
Nutrition experts have identified a disturbing pattern: fad diets don’t just fail, they spectacularly backfire by causing slowed metabolic rate, increased body fat storage, and heightened appetite. This creates a yo-yo effect that leaves dieters worse off than when they started.
The psychological manipulation works through:
- Quick wins: Initial water weight loss creates false hope
- Restriction psychology: Forbidden foods become more desirable
- All-or-nothing thinking: Minor slips trigger complete abandonment
- Blame shifting: Failure is attributed to lack of willpower, not flawed methods
Kate Hilton, Dietitian and founder of Diets Debunked, notes: “I’ve seen in my own clinical practice, multiple people who have gone down this path.” The damage goes beyond physical—it creates lasting psychological associations between food and failure.
Deconstructing Marketing’s Mind Games
Food companies employ teams of psychologists and neuroscientists to craft messages that bypass our rational thinking. Understanding these tactics is the first step toward immunity.
The “Natural” Fallacy
One of the most insidious examples involves protein supplements. Marketing campaigns successfully convinced consumers that natural protein sources are “full of chemicals” while positioning synthetic supplements as pure and necessary.
A nutritionist quoted in the analysis explains: “The claims are largely marketing-led, not science-backed. Protein isn’t ‘full of chemicals’ and isn’t just for bodybuilders. It’s essential, well-researched, and suitable for all age groups.”
Scientific-Sounding Nonsense
Marketers have learned to weaponize scientific language without scientific backing. Terms like “detox,” “superfood,” and “metabolism-boosting” sound credible but have no standardized definitions in nutrition science.
Common psychological triggers include:
- Authority positioning: “Doctor-recommended” (without specifying which doctors)
- Exclusivity claims: “Secret ingredient” or “ancient wisdom”
- Fear amplification: “Toxic buildup” that requires their solution
- Social proof manufacturing: Testimonials and before/after photos
Breaking Free from Nutritional Manipulation
The antidote to food marketing psychology isn’t more information—it’s developing meta-cognitive awareness of how our food beliefs form and persist.
Evidence-Based Reality Checks
The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics confirms that well-planned vegan diets provide adequate protein for all life stages, debunking another persistent myth about protein combining requirements.
The key principles for myth-resistant thinking include:
- Question the source: Who profits from this claim?
- Seek peer-reviewed research over marketing materials
- Be suspicious of dramatic promises or fear tactics
- Consider the biological plausibility of claims
- Remember that sustainable health changes are gradual
Rewiring Our Food Relationship
Understanding the psychology behind nutrition myths reveals something profound: our food choices are rarely about nutrition alone. They’re about identity, belonging, hope, and control in an uncertain world.
Research consistently shows that whole dairy products are associated with healthier weight in both children and adults, yet the low-fat myth persists because it’s become part of cultural identity around health consciousness.
The path forward isn’t about perfect nutritional knowledge—it’s about developing psychological immunity to manipulation while maintaining openness to legitimate scientific discovery. When we understand how our minds process food information, we can make choices based on evidence rather than engineered beliefs. The most powerful tool against food marketing isn’t skepticism—it’s the recognition that real nutrition science is rarely as dramatic or profitable as the myths designed to replace it.
You may like


What Drinking Water at the Wrong Time Does to Your Brain Is Shocking
Your Microwave Isn’t Killing Bacteria – The Kitchen Truth Will Shock You


Your Body’s Hidden Army of 4,000 Species Controls Your Mind


Award Shows’ Secret Power Over Your Choices Will Shock You


Your Sitting Position Does This to Your Spine – The Truth Revealed


How Street Art Secretly Rewires Your Brain and Transforms Cities
Food & Drink
Your Microwave Isn’t Killing Bacteria – The Kitchen Truth Will Shock You
Scientists reveal microwaves don’t sterilize food through radiation. Discover why your kitchen safety beliefs are wrong and how labs detect invisible bacterial threats.
Published
2 weeks agoon
January 19, 2026
Every day, 1 in 10 people worldwide fall ill from contaminated food, yet most of us believe our kitchens are safe havens protected by modern appliances and basic hygiene. The shocking reality? That microwave you rely on to zap bacteria isn’t actually sterilizing your food the way you think it does, and the invisible microscopic war raging in your kitchen is far more dangerous than you ever imagined.
The Staggering Scale of Our Invisible Food Safety Crisis
The numbers are more alarming than most people realize. According to the World Health Organization, approximately 420,000 adults and 125,000 children under 5 die annually from foodborne illnesses. This invisible pandemic affects 600 million people each year, making it one of the most underestimated public health challenges of our time.
What makes this crisis particularly insidious is that the pathogens responsible – including Salmonella, Listeria, and E. coli – are completely undetectable to the naked eye. They lurk on cutting boards, hide in refrigerator corners, and multiply on surfaces we consider clean. The European Food Safety Authority has established strict criteria for detecting these bacterial threats, yet they continue to slip through our home defense systems.
Why Your Kitchen Isn’t the Safe Zone You Think It Is
Cross-contamination occurs in ways most people never consider. That seemingly innocent act of placing your phone on the kitchen counter after handling raw chicken, or using the same sponge to wipe down multiple surfaces, creates pathways for bacteria to spread throughout your food preparation area.
The Great Microwave Myth: Why Heat Matters More Than Radiation
Here’s where most people’s understanding of food safety takes a dangerous turn. Hygiene Food Safety research reveals a startling truth: microwaves do not kill bacteria directly through radiation. Instead, they rely entirely on the generation of thermal energy.
“The reality is that microwaves do not kill bacteria directly; they rely on the generation of thermal energy. Without proper management, the microwave can become a vector for foodborne illness rather than a tool for prevention,” explains food safety research.
The Temperature Truth About Bacterial Elimination
For foodborne bacteria detection and elimination to be effective, food must reach specific internal temperatures:
- 165°F (74°C) for poultry and reheated leftovers
- 160°F (71°C) for ground meats
- 145°F (63°C) for whole cuts of beef and pork
- 145°F (63°C) for fish and shellfish
The problem? Microwaves create hot and cold spots, meaning parts of your food may never reach the temperature needed to eliminate dangerous bacteria, even when other parts are scalding hot.
Inside the Laboratory: How Scientists Hunt Invisible Bacterial Threats
While we struggle with basic food safety in our kitchens, food safety laboratories employ sophisticated bacterial contamination detection methods that would astound most home cooks. Modern laboratory detection methods can identify specific bacterial contamination in ready-to-eat foods using advanced microscopy techniques.
These high-tech facilities use:
- Electron microscopy to visualize bacteria at cellular levels
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) testing to identify bacterial DNA
- ATP bioluminescence to detect organic contamination
- Immunoassay techniques for rapid pathogen identification
The Race Against Time in Food Testing
What makes laboratory foodborne bacteria detection so crucial is the speed factor. Harmful bacteria can double their population every 20 minutes under ideal conditions. By the time traditional culture methods identify contamination, millions of bacteria may have already spread throughout food products.
The Perception Gap: What We Think vs. Reality in Kitchen Safety
The European Food Safety Authority has established comprehensive food safety criteria for detecting foodborne bacteria, yet most home kitchens operate without any systematic approach to bacterial prevention.
Common misconceptions include:
- Visual cleanliness equals bacterial safety – Surfaces can appear spotless while harboring millions of pathogens
- Refrigeration stops bacterial growth – Many bacteria, including Listeria, actually thrive in cold temperatures
- Cooking eliminates all food safety risks – Post-cooking contamination and improper storage can reintroduce dangers
- Natural foods are automatically safer – Fresh produce accounts for nearly half of all foodborne illness cases
The Cross-Contamination Web in Your Kitchen
Food safety experts have identified that most kitchen food safety breaches occur through seemingly innocent actions. Using the same cutting board for vegetables after cutting raw meat, storing leftovers at improper temperatures, or failing to wash hands between handling different ingredients creates an intricate web of contamination pathways.
Advanced Detection Methods: The Future of Food Safety
While home cooks rely on basic visual and smell tests, professional food safety has evolved to include revolutionary detection methods. Biosensors can now identify bacterial contamination in real-time, and portable devices are beginning to make laboratory-quality testing accessible outside traditional lab settings.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention research shows that many forms of bacterial poisoning can be prevented through proper hand washing, preventing cross-contamination, proper storage, and maintaining appropriate cooking temperatures – but only when these practices are implemented systematically and consistently.
The Role of Rapid Detection Technology
Emerging technologies in food safety bacteria detection include smartphone-based testing kits, AI-powered contamination prediction, and real-time monitoring systems that can alert users to potential bacterial threats before they become health hazards.
Practical Revolution: Transforming Your Kitchen Safety Protocols
Understanding the science behind foodborne illness prevention means completely rethinking your approach to kitchen safety. Instead of relying on assumptions and outdated methods, you can implement laboratory-inspired protocols in your home.
Evidence-based safety practices include:
- Temperature verification using digital thermometers for all reheated foods
- Time-sensitive storage protocols following the “2-hour rule” for perishable foods
- Dedicated cutting board systems preventing cross-contamination between raw and cooked foods
- Regular sanitization schedules using appropriate cleaning solutions for different surface types
The key insight from professional bacterial contamination detection is that prevention always outperforms treatment. By understanding how bacteria behave and spread, you can create systematic barriers that protect your family without requiring expensive equipment or laboratory expertise.
The microscopic war happening in your kitchen doesn’t have to be a losing battle. Armed with scientific understanding of how bacteria operate and spread, combined with proper detection awareness and prevention protocols, you can transform your kitchen from a potential contamination zone into a genuinely safe food preparation environment. The invisible threats are real, but so are the science-based solutions that can protect you from them.
Food & Drink
What Your Brain Actually Does When You Eat Comfort Food Is Shocking
Discover the hidden neuroscience behind comfort food cravings and why your brain treats familiar foods like emotional medicine during stress.
Published
2 weeks agoon
January 14, 2026
When you reach for that bowl of ice cream after a stressful day or crave your grandmother’s chicken soup when you’re feeling down, your brain is actually performing a sophisticated neurochemical operation that mirrors the effects of prescription medications. Comfort food psychology reveals that what we dismiss as simple emotional eating is actually your brain’s attempt to self-medicate through familiar flavors and textures.
Your Brain Treats Comfort Food Like Medicine
The moment you smell freshly baked cookies or taste that first spoonful of mac and cheese, your brain activates the same neural pathways used by antidepressants and anxiety medications. When we experience stress or negative emotions, our brains release cortisol and other stress hormones that create feelings of discomfort and unease.
Comfort foods trigger the release of serotonin and dopamine – the same neurotransmitters that pharmaceutical treatments target. This isn’t coincidence; it’s an evolutionary survival mechanism. Research from Psychology Today shows that eating is frequently used to soothe unpleasant emotions like stress, anxiety, boredom, anger, and depression.
The Neurochemical Response Explained
Here’s what happens in your brain during emotional eating:
- Familiar foods activate memory centers in the hippocampus
- The amygdala processes emotional associations with specific tastes
- Neurotransmitter release creates temporary feelings of calm and pleasure
- The prefrontal cortex registers the experience as “successful coping”
This process explains why comfort food provides genuine, albeit temporary, emotional relief. Your brain literally treats these foods as a form of emotional nutrition.
Why Childhood Foods Become Adult Emotional Anchors
The most powerful comfort foods are rarely random choices – they’re deeply connected to our earliest memories and experiences. During childhood, our brains create what neuroscientists call “comfort maps” – neural pathways that link specific foods with feelings of safety, love, and security.
When your mother made you soup when you were sick, or when you celebrated achievements with a special dessert, your developing brain was forming powerful associations between those foods and positive emotions. These neural connections remain active throughout life, which is why a simple grilled cheese sandwich can instantly transport you back to feeling cared for and protected.
The Science of Food Memory
Food and mood connections are strengthened through multiple sensory channels:
- Olfactory memory: Smell is directly connected to the limbic system, making food aromas powerful emotional triggers
- Textural comfort: The physical sensation of creamy, warm, or crunchy foods provides tactile reassurance
- Temperature associations: Hot foods often recall nurturing experiences, while cold treats may evoke celebration memories
- Visual cues: The appearance of familiar foods can trigger anticipatory pleasure responses
This multisensory approach explains why comfort food science shows that certain dishes provide more emotional satisfaction than others, regardless of their nutritional content.
Modern Stress Triggers and Eating Patterns
Today’s fast-paced lifestyle creates unprecedented opportunities for stress eating. Unlike our ancestors who faced occasional acute stressors, modern humans deal with chronic, low-level stress that continuously activates our comfort-seeking behaviors.
Groundbreaking research published in ScienceDaily reveals that “experiencing psychological distress associated with living in lower socio-economic circumstances is associated with emotional eating to cope, which in turn is associated with obesity.”
Common Modern Triggers
These everyday situations frequently activate our food coping mechanism responses:
- Work deadlines and professional pressure
- Financial concerns and economic uncertainty
- Social media comparison and digital overwhelm
- Relationship conflicts and social isolation
- Information overload and decision fatigue
During these moments, our brains automatically seek the fastest route to emotional relief, often leading us to reach for familiar, calorie-dense foods that provide immediate neurochemical comfort.
The Multisensory Experience of Emotional Relief
Understanding comfort food psychology requires recognizing that emotional eating engages all five senses simultaneously. This comprehensive sensory experience is what makes comfort foods so effective at providing psychological relief.
When you bite into warm chocolate chip cookies, your brain processes multiple comfort signals at once: the sweet aroma triggers positive memories, the warm temperature suggests nurturing care, the soft texture provides oral comfort, and the familiar taste activates reward pathways. This sensory symphony creates a powerful emotional experience that temporarily overwhelms stress signals.
Breaking Down the Sensory Impact
Clinical research from YAVA shows that during stress, food provides comfort and a calming effect through multiple channels:
- Taste: Sweet and salty flavors activate immediate pleasure responses
- Smell: Familiar aromas trigger memory-based emotional associations
- Texture: Smooth, creamy, or crunchy textures provide physical comfort
- Temperature: Warm foods suggest care and nurturing
- Sound: The crunch of chips or sizzle of cooking activates anticipatory pleasure
Building Mindful Emotional Eating Habits
Recognizing that emotional eating serves a legitimate psychological function is the first step toward developing a healthier relationship with comfort foods. Rather than fighting these natural impulses, experts recommend building awareness and developing more mindful approaches to emotional nutrition.
University Hospitals research suggests that “when you slow down and savor the experience of eating something you truly enjoy, it’ll give you more emotional satisfaction, even with a small amount of that food.”
Strategies for Mindful Comfort Eating
- Practice emotional awareness: Identify the specific emotion triggering food cravings
- Choose quality over quantity: Select smaller portions of truly satisfying comfort foods
- Engage all senses: Eat slowly and pay attention to taste, texture, and aroma
- Create positive food rituals: Establish calming environments for emotional eating moments
- Build emotional resilience: Develop alternative coping strategies alongside food-based comfort
The Future of Emotional Nutrition
As our understanding of comfort food science continues to evolve, researchers are discovering that the relationship between food and emotion is far more complex and important than previously understood. Rather than viewing emotional eating as a weakness or failure, emerging research suggests that mindful emotional nutrition can be part of a healthy psychological toolkit.
The key lies not in eliminating comfort foods entirely, but in understanding their role as emotional nutrition and developing more conscious, balanced approaches to using food for psychological comfort. When we recognize that our brains genuinely benefit from the neurochemical relief that familiar foods provide, we can make more informed choices about when, how, and why we turn to comfort eating.
By understanding the hidden science behind our comfort food cravings, we can transform what might seem like mindless emotional eating into a more conscious, self-compassionate approach to managing life’s inevitable stresses and emotional challenges.
Food & Drink
Your Favorite Pickle Brand’s Shocking Secret Will Change Everything
Think your store-bought pickles are healthy fermented foods? The truth about what you’re really eating will completely transform your grocery shopping forever.
Published
3 weeks agoon
January 13, 2026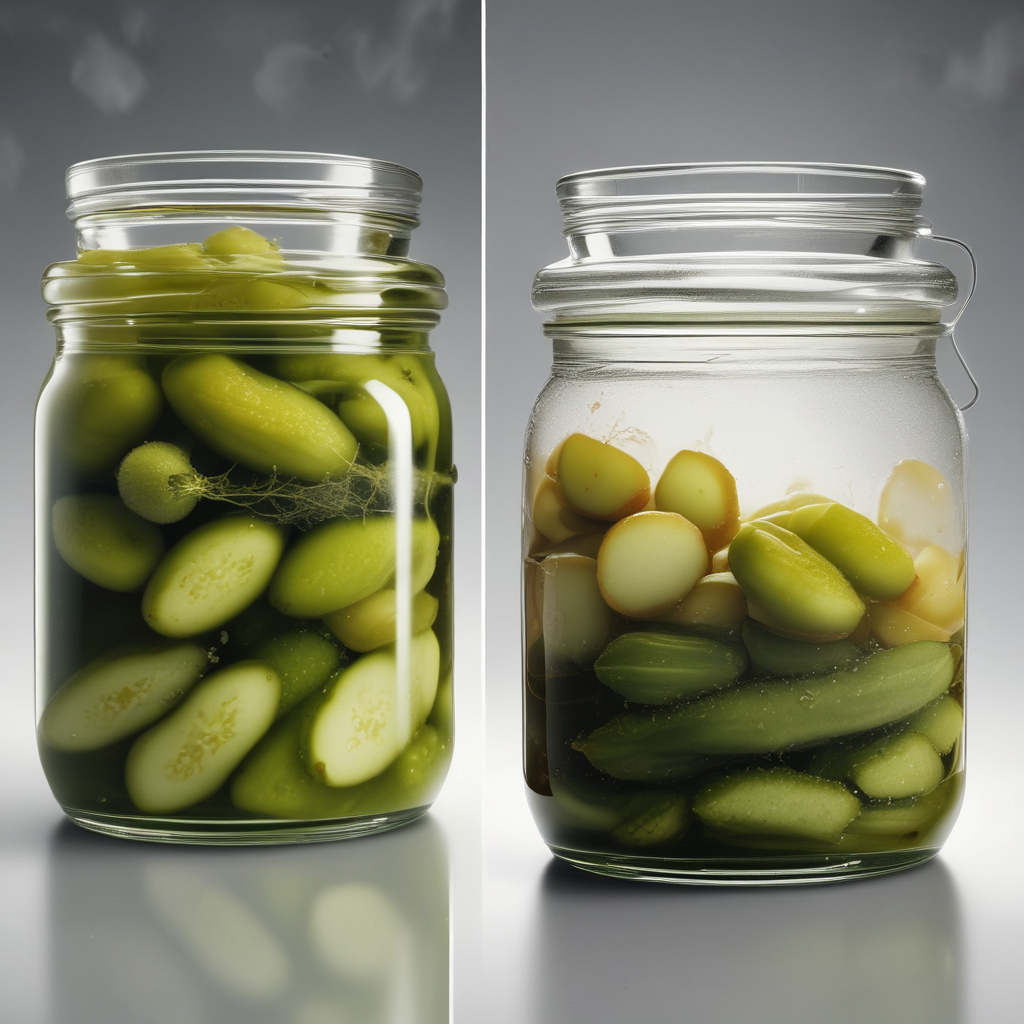
Next time you bite into a Vlasic pickle, you’re eating something fundamentally different from what your great-grandmother called a “pickle.” While she waited weeks for naturally fermented vegetables teeming with beneficial bacteria, you’re consuming what food scientists call a “dead” product—devoid of the living cultures that made traditional pickles a health food.
The Great Divide: True Fermentation vs. Industrial Pickling
The confusion starts with terminology. Both processes are called “pickling,” but they’re as different as living yogurt and artificial flavoring. True fermented pickles use only salt brine and time—typically 3-4 weeks at 70-75°F—allowing naturally occurring Lactobacillus bacteria to convert sugars into lactic acid.
Commercial brands like Vlasic take a completely different approach, submerging vegetables in pre-made vinegar solutions that create shelf-stable products in hours, not weeks.
The Time Factor Reveals Everything
- Traditional fermentation: 3-4 weeks minimum
- Commercial pickling: Hours to days
- Living cultures: Fermented only
- Shelf stability: Commercial advantage
The Science Behind the Deception: How Vinegar Kills What Salt Preserves
Here’s where the science gets fascinating. Vinegar’s high acidity immediately kills microorganisms—including the beneficial bacteria that your digestive system craves. The USDA confirms that this acidic environment prevents any probiotic development, meaning those pickles offer zero gut health benefits.
Meanwhile, salt-brine fermentation creates the opposite environment. The controlled salinity encourages beneficial bacteria while inhibiting harmful pathogens. As naturally occurring bacteria consume sugars in the vegetables, they slowly produce lactic acid, creating a living ecosystem in every jar.
The Living vs. Dead Food Reality
Food fermentation experts describe this as the difference between “living” and “dead” foods. Fermented vegetables continue changing and developing flavors because they contain active cultures, while vinegar pickles remain static—preserved but lifeless.
Commercial Reality Check: Why Brands Choose Speed Over Probiotics
The shift from fermentation to vinegar pickling wasn’t accidental. As food manufacturing scaled up in the 20th century, companies needed predictable, consistent products with extended shelf lives. Fermentation is inherently variable—temperature, humidity, and bacterial cultures can create slight differences between batches.
Vinegar pickling solved these problems instantly. Manufacturers could produce identical-tasting pickles year-round, store them at room temperature for months, and eliminate the risk of fermentation “failures.” The trade-off? Eliminating every health benefit that made pickles valuable beyond their taste.
The Profit Motive Behind Your “Pickles”
Consider the economics: fermented pickles require 3-4 weeks of production time, specialized storage, and refrigerated distribution. Vinegar pickles can go from cucumber to shelf in days, store at room temperature, and have virtually unlimited shelf life. For massive food corporations, the choice was obvious.
How to Identify and Find Real Fermented Pickles
The good news? You can easily identify genuine fermented pickles by following a few key indicators:
The Refrigeration Test
Real fermented pickles must be refrigerated to keep beneficial bacteria alive. If you find pickles in the shelf-stable aisle, they’re vinegar-pickled. Brands like Bubbies maintain refrigeration throughout distribution to preserve probiotic integrity.
Reading the Label Like a Pro
- Look for: “Naturally fermented,” “Contains live cultures,” or “Unpasteurized”
- Avoid: Vinegar as a primary ingredient
- Check ingredients: Should list salt, water, vegetables, and spices—nothing else
- Price indicator: Genuine fermented pickles typically cost more due to time and refrigeration requirements
The Bubble Test
Authentic fermented pickles often show small bubbles in the brine—evidence of ongoing fermentation. This “activity” is exactly what commercial brands eliminate through pasteurization and vinegar processing.
What This Means for Your Health and Wallet
If you’ve been buying commercial pickles expecting probiotic benefits, you’re getting none of the digestive health advantages that make fermented foods valuable. Those beneficial bacteria that support gut health, boost immunity, and aid digestion simply don’t exist in vinegar-processed products.
However, this doesn’t make store-bought pickles “bad”—they’re just different products serving different purposes. Vinegar pickles offer convenience, consistent flavor, and long-term storage without refrigeration. The deception lies in marketing and consumer expectations, not the products themselves.
Understanding this difference empowers you to make informed choices. Want convenience and familiar taste? Commercial pickles deliver. Seeking probiotic benefits and traditional fermentation? Look for refrigerated, naturally fermented options—or better yet, try making your own using traditional salt-brine methods that have preserved food and health for thousands of years.

Why Emergency Alerts Fail When You Need Them Most – The Truth

Why Your City’s Name Isn’t What You Think – The Hidden Truth Revealed

Ancient Persia’s Secret Weapon That Built History’s First Superpower

Hidden Economic Warfare: How Climate Deals Secretly Control Global Trade

7 Anonymous Heroes Who Changed History Forever – 3 Will Shock You

Scientists Just Discovered What Renaissance Artists Knew All Along – It Changes Everything
Trending

 Global News1 month ago
Global News1 month agoHidden Economic Warfare: How Climate Deals Secretly Control Global Trade

 Historical Figures2 months ago
Historical Figures2 months ago7 Anonymous Heroes Who Changed History Forever – 3 Will Shock You
 Art & Design2 months ago
Art & Design2 months agoScientists Just Discovered What Renaissance Artists Knew All Along – It Changes Everything

 Fun Facts2 months ago
Fun Facts2 months agoScientists Just Discovered Space Isn’t Silent – The Sounds Will Shock You
 Global News3 months ago
Global News3 months agoUndefined Behavior Programming: The Hidden Digital Threat

 News & World2 months ago
News & World2 months agoUrban Explorers’ Most Terrifying Encounters in ‘Empty’ Buildings

 Lifestyle & Culture2 months ago
Lifestyle & Culture2 months agoScientists Just Discovered What 1-Minute Workouts Do to Your Body (Mind-Blowing Results)

 News & World2 months ago
News & World2 months ago7 Bizarre Travel Destinations That Defy All Logic (Scientists Are Baffled)

