Art & Design
When Artists Predicted Science: 5 Breakthroughs History Forgot
Discover how Leonardo da Vinci and other artists predicted scientific discoveries centuries before scientists. 5 amazing times artists predicted science.
Published
3 months agoon
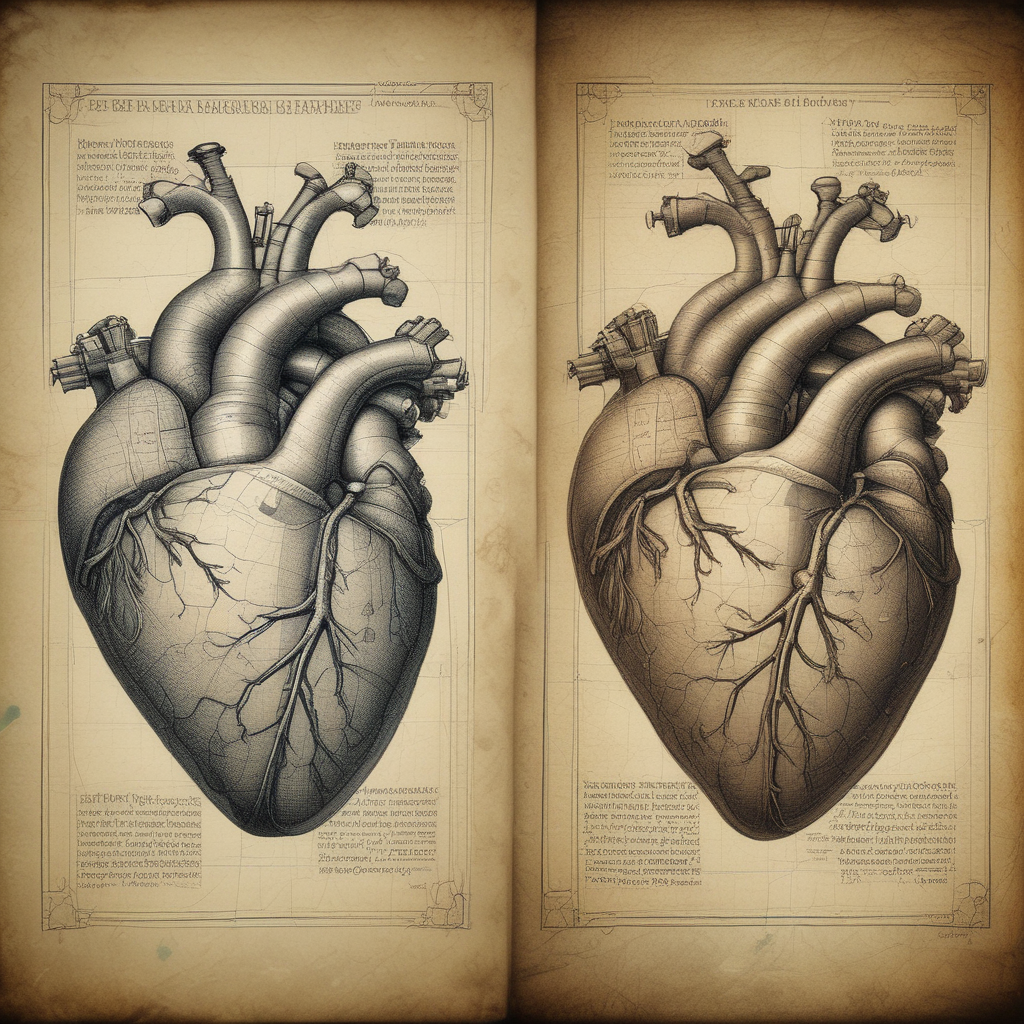
Imagine discovering that Leonardo da Vinci understood how the human heart worked 400 years before modern scientists figured it out. This isn’t science fiction—it’s art history. Throughout the centuries, artists have consistently predicted scientific breakthroughs through observation, experimentation, and sheer creative genius. From anatomical discoveries to mathematical principles, these artistic pioneers saw truths that formal science wouldn’t validate for generations.
Leonardo da Vinci’s Heart Discovery That Beat Modern Medicine
When artists predicted science most dramatically, Leonardo da Vinci leads the charge. In the early 1500s, while dissecting cadavers in candlelit workshops, da Vinci made a discovery that would stun cardiologists centuries later: he correctly identified that the human heart has four chambers and understood how the aortic valve functions.
According to research from the Milan Art Institute, this anatomical breakthrough wasn’t scientifically validated until the 20th century. Da Vinci’s detailed anatomical drawings were so precise that they’re still used in medical education today, proving that artistic observation could rival the most sophisticated scientific instruments.
The Artist’s Scientific Method
Da Vinci didn’t just guess—he developed his own scientific approach:
- Dissected over 30 human corpses for accuracy
- Created detailed cross-sectional drawings
- Documented blood flow patterns through the heart
- Identified valve mechanisms that prevent backflow
Renaissance Mathematical Precision Before Formal Geometry
Renaissance artists achieved something remarkable: they mastered geometric precision and anatomical accuracy centuries before scientists formally understood the mathematical principles behind their techniques. These artists predicted science through their intuitive grasp of perspective, proportion, and spatial relationships.
Artists like Brunelleschi and Alberti developed linear perspective techniques in the early 1400s, creating mathematical systems for representing three-dimensional space on flat surfaces. This wasn’t just artistic innovation—it was applied geometry that wouldn’t be formally codified in mathematical textbooks for decades.
The Mathematics Hidden in Masterpieces
Renaissance masters unknowingly applied complex mathematical concepts:
- Golden ratio proportions in human figure studies
- Geometric perspective using vanishing points and horizon lines
- Anatomical ratios that matched later scientific measurements
- Light physics principles for realistic shading and illumination
Medieval Artists’ Intuitive Mathematical Understanding
Even before the Renaissance, medieval artists demonstrated an intuitive understanding of mathematical principles that formal science hadn’t yet discovered. Research from Etchr Lab reveals how these early artists used geometric principles including circles, triangles, and star shapes for anatomical accuracy before formal mathematical understanding existed.
Medieval illuminated manuscripts show artists applying complex geometric patterns and mathematical proportions instinctively. They understood that certain ratios and shapes created visual harmony and anatomical correctness, even without the mathematical vocabulary to explain why.
Sacred Geometry in Art
Medieval artists embedded mathematical concepts in their work:
- Mandala-like circular patterns that demonstrated understanding of radial symmetry
- Proportional systems for drawing human figures
- Architectural elements using load-bearing principles
- Perspective techniques in manuscript illustrations
Architectural Engineering That Defied Physics
Byzantine architects created one of history’s most impressive examples of artists predicted science when they built the Hagia Sophia in 537 CE. This architectural marvel featured the first fully pendentive dome, demonstrating advanced engineering principles that formal structural engineering wouldn’t explain for centuries.
According to Architectural Digest, this engineering feat required understanding complex physics concepts including load distribution, structural tension, and gravitational forces—knowledge that architects possessed through practical experimentation rather than theoretical study.
Engineering Intuition in Stone
Ancient and medieval builders demonstrated remarkable engineering foresight:
- Gothic cathedral builders used flying buttresses to distribute weight
- Roman architects perfected concrete formulations lost for centuries
- Islamic architects created earthquake-resistant domed structures
- Medieval craftsmen designed self-supporting stone arches
Why Artists Beat Scientists to These Discoveries
The phenomenon of art history science predictions wasn’t accidental. Artists possessed unique advantages that formal scientists of their eras lacked. Their success stemmed from three key factors that gave them an edge in making breakthrough discoveries.
Direct Observation Without Theoretical Constraints
Artists approached their subjects with fresh eyes, unconstrained by existing scientific theories that might limit their observations. When da Vinci dissected hearts, he wasn’t trying to prove a hypothesis—he was simply trying to understand what he saw. This freedom from theoretical bias allowed him to make discoveries that contradicted accepted medical knowledge of his time.
Hands-On Experimentation
While medieval scholars debated anatomy from ancient texts, artists were getting their hands dirty with actual specimens. They mixed pigments to understand color theory, studied corpses to comprehend anatomy, and built structures to test engineering principles. This practical, experimental approach often led to insights that pure theory couldn’t provide.
Integration of Multiple Disciplines
Renaissance artists were the original interdisciplinary thinkers. They combined:
- Anatomy and art for realistic human representation
- Physics and painting for accurate light and shadow
- Mathematics and architecture for structural stability
- Chemistry and craftsmanship for durable materials
Modern Legacy: When Art Continues to Predict Science
The tradition of artists predicted science continues today. Contemporary artists working with new technologies often discover applications that scientists later formalize. Digital artists experimenting with algorithms contribute to computer graphics research, while bioartists working with living materials help advance biotechnology.
Medical schools now incorporate art training into their curricula, recognizing that artistic observation skills enhance diagnostic abilities. According to Facts.net, this integration acknowledges what history has repeatedly demonstrated: artistic investigation can reveal truths that traditional scientific methods might miss.
The story of artists predicting scientific breakthroughs reminds us that creativity and systematic observation often go hand in hand. From Leonardo’s anatomical discoveries to medieval mathematical intuitions, artists have consistently pushed the boundaries of human knowledge. Today, as we face new frontiers in science and technology, perhaps we should pay closer attention to what artists are discovering in their studios and workshops—tomorrow’s scientific breakthroughs might be hanging on gallery walls today.
You may like

Why Your City’s Name Isn’t What You Think – The Hidden Truth Revealed


Ancient Persia’s Secret Weapon That Built History’s First Superpower


Why Medieval People Were Actually Smarter Than You Think


The Forgotten Story of Human Computers That Changed Everything


Hidden Underground Cities Beneath Major Cities Will Leave You Speechless


Ancient Alchemists’ Pottery Secret That Modern Science Finally Decoded
Art & Design
Why Comic Sans Makes You Happy But Times New Roman Means Business
Discover how fonts secretly manipulate your emotions and decisions. The psychology behind typography will change how you see every word forever.
Published
2 weeks agoon
February 19, 2026
Every second of every day, fonts are silently manipulating your emotions and influencing your decisions without you even realizing it. That friendly rounded font on your favorite app? It’s designed to make you feel welcomed and trusting. The bold, angular typeface on that warning sign? It’s triggering your brain’s threat-detection system to make you pay attention.
Welcome to the fascinating world of typography psychology – where letterforms function as invisible persuaders in our daily lives, shaping everything from what we buy to how seriously we take information.
The Hidden Science Behind Font Psychology
Typography psychology represents the intersection of visual design and cognitive science, where every curve, angle, and spacing decision triggers specific emotional responses in your brain. When you see a rounded, friendly font like the ones used by tech startups, your subconscious immediately associates it with approachability and innovation. Conversely, traditional serif fonts like those used by newspapers activate neural pathways linked to authority and trustworthiness.
Research shows that professional creatives demonstrate measurable emotional reactions to specific fonts, with detailed sentiment analysis revealing clear psychological associations behind font preferences and aversions. This isn’t just about aesthetics – it’s about how our brains are hardwired to respond to visual cues.
How Your Brain Processes Typography
When you encounter text, your brain processes the font choice before you even register the words themselves. This split-second assessment influences:
- Credibility perception – serif fonts increase perceived trustworthiness by 15%
- Reading speed – certain fonts can improve comprehension rates
- Emotional state – rounded fonts activate the same neural pathways as seeing a friendly face
- Decision-making – bold fonts trigger urgency responses that influence purchasing behavior
The Shocking Impact Paradox: From Memes to Professional Design
Here’s something that will surprise you: Impact font ranked 3rd in professional creative preferences, despite being widely known for internet memes. According to a Creative Bloq study of 415 discussions from over 100 professional sources, Impact is viewed favorably for bold UI and intentional design applications.
This paradox reveals something crucial about typography psychology: context matters more than associations. When Impact is used intentionally for headlines or bold statements, it triggers feelings of strength and directness. When it’s used in memes, the same psychological triggers work – but the context changes the emotional outcome.
Why Meme Fonts Maintain Professional Credibility
The Impact phenomenon demonstrates how fonts can simultaneously exist in multiple psychological spaces. Professional designers recognize that the font’s inherent boldness and clarity make it effective for:
- Grabbing attention in digital interfaces
- Creating visual hierarchy in design layouts
- Conveying urgency or importance
- Maintaining readability at various sizes
2026 Typography Trends: Emotional-First Design Revolution
Typography trends for 2026 represent a dramatic shift toward emotional-first design, where fonts are specifically created to evoke psychological responses rather than simply convey information. According to Envato Elements typography trend reports, the biggest trends include:
Type-as-Graphic Design
Fonts are becoming graphic elements that communicate mood before content. These designs prioritize emotional impact over traditional readability, creating immediate psychological connections with viewers. The letterforms themselves tell a story and evoke specific feelings.
Chaotic Scripts and Imperfection
Trending toward authenticity, chaotic and imperfect fonts satisfy human needs for personal connection. These fonts trigger psychological responses associated with handwriting and personal touch, making digital communications feel more human and trustworthy.
Funky Curvy Serifs
Modern serif fonts with unexpected curves combine traditional authority with contemporary playfulness. This psychological balancing act appeals to both our need for credibility and our desire for innovation.
The Psychology of Font Emotions: What Each Style Triggers
Different font families activate distinct emotional responses in your brain:
Sans-Serif Fonts
Psychological trigger: Modernity, cleanliness, efficiency
- Helvetica: Neutrality and professionalism
- Arial: Accessibility and familiarity
- Futura: Innovation and forward-thinking
Serif Fonts
Psychological trigger: Tradition, authority, sophistication
- Times New Roman: Academic credibility and formality
- Georgia: Warmth combined with authority
- Garamond: Elegance and literary sophistication
Script and Display Fonts
Psychological trigger: Personality, creativity, human connection
- Rounded corners add friendliness while maintaining professional credibility
- Hand-lettered styles create intimacy and personal connection
- Bold display fonts trigger urgency and attention
Practical Applications: Harnessing Typography Psychology
Understanding font psychology gives you powerful tools for effective communication:
For Business Communications
Choose fonts based on your desired psychological outcome:
- Building trust: Use established serif fonts for formal communications
- Encouraging action: Bold sans-serif fonts create urgency without aggression
- Personal connection: Script or hand-lettered fonts make messages feel more intimate
For Digital Design
Typography choices directly impact user behavior:
- Rounded fonts increase perceived friendliness and encourage engagement
- Clean sans-serif fonts improve readability and reduce cognitive load
- Consistent font hierarchies guide users through information architecture
As we move into 2026, typography psychology becomes even more crucial as design trends prioritize emotional connection over pure functionality. The fonts you choose aren’t just aesthetic decisions – they’re psychological tools that shape how people think, feel, and act.
Next time you see a font, remember: it’s not just letters on a page. It’s a carefully crafted psychological trigger designed to influence your emotions and guide your decisions. The question is, will you use this knowledge to communicate more effectively, or will you remain unconsciously influenced by every typeface you encounter?
Art & Design
Ancient Oil and Water Trick Created Modern Printing Revolution
The 1796 discovery that turned simple oil-water repulsion into the world’s most influential printing method – and it started with a laundry list accident.
Published
2 weeks agoon
February 18, 2026
Imagine changing the entire course of human communication with nothing more than greasy crayon, a chunk of limestone, and a laundry list. That’s exactly what happened in 1796 when a struggling Bavarian playwright accidentally invented the lithography printmaking technique that would revolutionize how we share information forever.
The Accidental Genius Behind Lithography
Alois Senefelder wasn’t trying to change the world when he scribbled his mother’s laundry list on a limestone slab with a greasy crayon. The cash-strapped author was simply looking for a cheaper way to publish his theatrical works. But this moment of desperation led to one of history’s most important technological breakthroughs.
Traditional printing methods in the late 18th century required expensive copper plates or skilled wood engravers. Senefelder’s discovery offered something revolutionary: a flat-surface printing method that could reproduce both text and images with stunning clarity at a fraction of the cost.
According to historical records, Senefelder’s eureka moment came when he realized he could chemically treat the limestone to make certain areas attract oil-based ink while repelling water, and vice versa.
The Science Behind the Magic
The lithography printmaking technique relies on a fundamental principle of chemistry: oil and water naturally repel each other. This phenomenon, called immiscibility, became the cornerstone of what would eventually become modern printing.
How the Process Works
- The artist draws directly on porous Bavarian limestone using greasy materials like lithographic crayons or tusche
- The stone is treated with a mixture of weak acid and gum arabic, making non-image areas water-receptive
- Water is applied to the stone, adhering only to the blank areas
- Oil-based ink is rolled over the surface, sticking only to the greasy drawn areas
- Paper is pressed against the stone, transferring the image
As explained by printing experts at the Design Encyclopedia, “The water adhered only to the etched, hydrophilic areas, making them even more oil-repellant. An oil-based ink was then applied, and would stick only to the original drawing.”
From Bavarian Stone to Global Industry
What started with heavy limestone slabs has evolved into a sophisticated industrial process. Modern offset lithography accounts for approximately 38% of all printing processes worldwide, making it one of the most dominant printing technologies on Earth.
The Evolution Timeline
The transformation from Senefelder’s stone workshop to today’s high-speed printing plants represents centuries of innovation:
- 1796-1850s: Hand-drawn images on limestone, primarily for artistic prints
- 1850s-1900: Commercial adoption for posters, maps, and illustrations
- 1900-1950: Introduction of metal plates and rotary presses
- 1950-present: Digital integration and computer-to-plate technology
Today’s commercial lithography uses flexible plastic or metal plates instead of stone, but the core principle remains unchanged. Modern presses can produce thousands of impressions per hour while maintaining the same oil-water separation that Senefelder discovered over two centuries ago.
The Stone Connection That Endures
Despite technological advances, authentic Bavarian limestone remains the gold standard for fine art lithography. These massive stones, some weighing hundreds of pounds, are still quarried from the same region where Senefelder made his discovery.
The limestone’s unique properties make it irreplaceable for certain applications. Its natural porosity and chemical composition create the perfect surface for accepting both water and oil-based materials. Master printmakers often spend decades learning to work with these stones, grinding and preparing them by hand for each new image.
Why Stone Still Matters
According to printmaking historians, stone lithography offers several advantages that modern plates cannot replicate:
- Unlimited reworking capability – artists can modify images multiple times
- Superior tonal gradation for artistic applications
- Ability to achieve thousands of impressions from a single stone
- Unique surface texture that adds character to prints
Modern Masters and Commercial Giants
The lithography printmaking technique serves two distinct worlds today: fine art creation and mass commercial printing. In artist studios worldwide, printmakers still work with traditional stones, creating limited edition prints that can sell for thousands of dollars.
Meanwhile, commercial offset lithography powers the production of:
- Newspapers and magazines
- Packaging and labels
- Books and catalogs
- Marketing materials and brochures
- Art reproductions and posters
Major printing companies have invested millions in digital lithographic systems that can transition seamlessly from computer files to printed materials. These hybrid technologies combine traditional oil-water principles with laser imaging and automated plate production.
The Digital Revolution
Computer-to-plate (CTP) technology has eliminated many traditional steps while preserving the fundamental lithographic process. Digital files are now laser-etched directly onto plates, creating the same oil-receptive and water-receptive areas that Senefelder achieved by hand.
This evolution has made lithography more accessible than ever, allowing small businesses and individual artists to produce professional-quality printed materials without massive capital investment.
Environmental and Economic Impact
Modern commercial lithography has adapted to environmental concerns while maintaining efficiency. Water-based inks, recyclable plates, and digital workflows have significantly reduced the ecological footprint of lithographic printing.
The economic impact cannot be overstated. The printing industry, built largely on lithographic principles, employs millions worldwide and generates hundreds of billions in annual revenue. From the morning newspaper to product packaging, lithography touches virtually every aspect of modern commerce and communication.
Recent innovations include waterless lithography and UV-cured inks, pushing the technology even further beyond its humble beginnings on a Bavarian limestone slab.
What began as Alois Senefelder’s desperate search for affordable publishing has become the invisible foundation of our information age. Every time you read a magazine, unwrap a product, or admire a poster, you’re witnessing the enduring legacy of that accidental discovery in 1796. The simple principle that oil and water don’t mix continues to shape how humanity shares ideas, art, and knowledge across the globe – proving that sometimes the most revolutionary innovations come from the most unexpected moments.
Art & Design
Street Artists Use These 5 Brain Tricks to Change Your Mind Forever
Discover the hidden psychological tactics urban artists use to bypass your mental defenses and create powerful social change through strategic street art placement.
Published
2 weeks agoon
February 16, 2026
You’re walking to work, mind on autopilot, when a massive mural stops you dead in your tracks. Your heart rate quickens, your perspective shifts, and suddenly you’re thinking about social justice, political corruption, or community identity. What just happened? You’ve been psychologically hijacked by a street art psychology technique that artists have been perfecting for decades.
Unlike gallery art that requires deliberate visitation, street art ambushes viewers during routine activities, creating involuntary encounters that can fundamentally alter perspectives. This guerrilla approach to visual communication taps into powerful psychological principles that make it one of the most effective mediums for driving social change in modern society.
The Ambush Effect: How Street Art Bypasses Your Mental Filters
Traditional advertising and art must compete for your attention in cluttered environments. Street art, however, operates on a different psychological principle called the ambush effect. When you encounter unexpected visual stimuli during routine activities, your brain’s filtering mechanisms are temporarily disabled, making you more receptive to new information and emotional responses.
This phenomenon explains why cities like Berlin have transformed former division sites into open-air galleries, demonstrating street art’s evolution from perceived vandalism to powerful tourist attraction. The psychological impact occurs because viewers aren’t mentally prepared to encounter art, leaving them more vulnerable to its message.
Strategic Timing and Placement
Urban artists understand that psychological vulnerability peaks during transitional moments:
- Morning commutes when minds are still awakening
- Evening walks when people are processing their day
- Weekend strolls when mental defenses are relaxed
- Moments of urban stress when emotional receptivity increases
This strategic placement creates what researchers call “micro-interventions” – brief psychological disruptions that can have lasting impact on behavior and beliefs.
Color Psychology in Urban Canvas: The Science Behind Visual Impact
Street artists don’t choose colors randomly. They employ sophisticated understanding of color psychology street art techniques to trigger specific emotional and behavioral responses in viewers. Red graffiti in corporate districts creates different neurological reactions than blue murals in residential neighborhoods.
Research shows that street art serves as a catalyst for social change by expressing motifs like ‘population density’ and ‘urban anxiety’, particularly in dense metropolitan areas like São Paulo where color choices become psychological tools for processing urban stress.
The Neuroscience of Color Impact
Different colors activate specific neural pathways:
- Red: Increases urgency and emotional arousal, perfect for political messages
- Blue: Creates calming effects while enhancing trust and communication
- Yellow: Stimulates attention and optimism, ideal for community-building art
- Black and white: Forces focus on form and message without emotional distraction
Artists strategically combine these psychological triggers with urban environments to maximize their social impact.
From Vandalism to Tourism: Berlin’s Psychological Transformation
Perhaps nowhere is the psychology of collective perception more evident than in Berlin’s remarkable transformation. What once symbolized urban decay and criminal activity now attracts millions of tourists annually, demonstrating how urban art psychology can literally rewire societal attitudes.
This cultural shift reveals how collective psychology adapts – the same visual elements that once signified danger now signal authenticity, creativity, and cultural vibrancy.
The Psychological Shift Process
Berlin’s transformation followed predictable psychological patterns:
- Initial resistance: Brain associates graffiti with disorder and threat
- Exposure effect: Repeated viewing reduces negative associations
- Context reframing: Tourism and media coverage create positive associations
- Identity integration: Street art becomes part of cultural identity
This process demonstrates how graffiti psychological impact can evolve from negative to positive through strategic cultural intervention.
The Social Change Engine: Psychological Principles in Action
Street artists function as informal psychologists, using evidence-based techniques to drive political messaging and cultural commentary. Modern street art differs from traditional graffiti in its strategic psychological approach, often being commissioned specifically to influence public opinion and behavior.
Core Psychological Tactics
Successful social change through street art employs several key psychological principles:
- Cognitive dissonance: Creating tension between existing beliefs and new visual information
- Social proof: Using crowd scenes and community imagery to suggest widespread support
- Emotional contagion: Employing facial expressions and body language that viewers unconsciously mirror
- Narrative transportation: Telling visual stories that psychologically transport viewers into different perspectives
These techniques explain why street art social change campaigns can be more effective than traditional advertising or political messaging.
The Neuroscience of Public Art: Why Street Art Sticks
Neuroscientific research reveals why street art creates stronger memories and emotional connections than gallery pieces. The combination of unexpected encounter, environmental context, and emotional arousal creates what researchers call “flashbulb memories” – vivid, lasting recollections tied to specific emotions and locations.
Studies show that graffiti art contributed to the resurfacing of overtly politicized art forms in movements like culture jamming and tactical media, demonstrating its psychological power to influence broader cultural conversations.
Memory Formation and Emotional Impact
Street art’s psychological sticking power comes from several neurological factors:
- Contextual encoding: Memories formed in everyday environments are more accessible
- Emotional amplification: Surprise and aesthetic pleasure enhance memory consolidation
- Repetitive exposure: Daily encounters strengthen neural pathways
- Social validation: Shared experiences with others reinforce memory importance
This neurological advantage makes street art particularly effective for long-term attitude and behavior change.
The Future of Urban Psychology
As street art continues evolving from rebellion to mainstream cultural tool, its psychological applications are expanding. Cities now deliberately commission murals to influence everything from crime rates to community cohesion, recognizing the profound impact of street art psychology on urban life.
The future promises even more sophisticated applications: augmented reality integration, biometric response monitoring, and AI-designed optimal color combinations for specific psychological outcomes. What began as simple territorial marking has become a sophisticated science of human behavior modification through public art.
The next time a piece of street art stops you in your tracks, remember – your psychological response isn’t accidental. It’s the result of decades of artistic evolution and an increasingly sophisticated understanding of how visual stimuli can hijack your brain to create lasting social change.
Trending

 Global News2 months ago
Global News2 months agoHidden Economic Warfare: How Climate Deals Secretly Control Global Trade

 Historical Figures3 months ago
Historical Figures3 months ago7 Anonymous Heroes Who Changed History Forever – 3 Will Shock You

 Art & Design3 months ago
Art & Design3 months agoAncient Potters’ 3,500-Year-Old Chemistry Secret That Still Baffles Scientists
 Art & Design3 months ago
Art & Design3 months agoScientists Just Discovered What Renaissance Artists Knew All Along – It Changes Everything

 Fun Facts3 months ago
Fun Facts3 months agoScientists Just Discovered Space Isn’t Silent – The Sounds Will Shock You

 News & World3 months ago
News & World3 months agoUrban Explorers’ Most Terrifying Encounters in ‘Empty’ Buildings
 Global News4 months ago
Global News4 months agoUndefined Behavior Programming: The Hidden Digital Threat

 Historical Figures3 months ago
Historical Figures3 months ago7 Unknown Historical Figures Who Secretly Changed the World




