News & World
Hidden Underground Cities Beneath Major Cities Will Leave You Speechless
Discover the secret world of abandoned tunnels, military bunkers, and forgotten underground spaces hiding beneath busy city streets that most people never know exist.
Published
2 weeks agoon
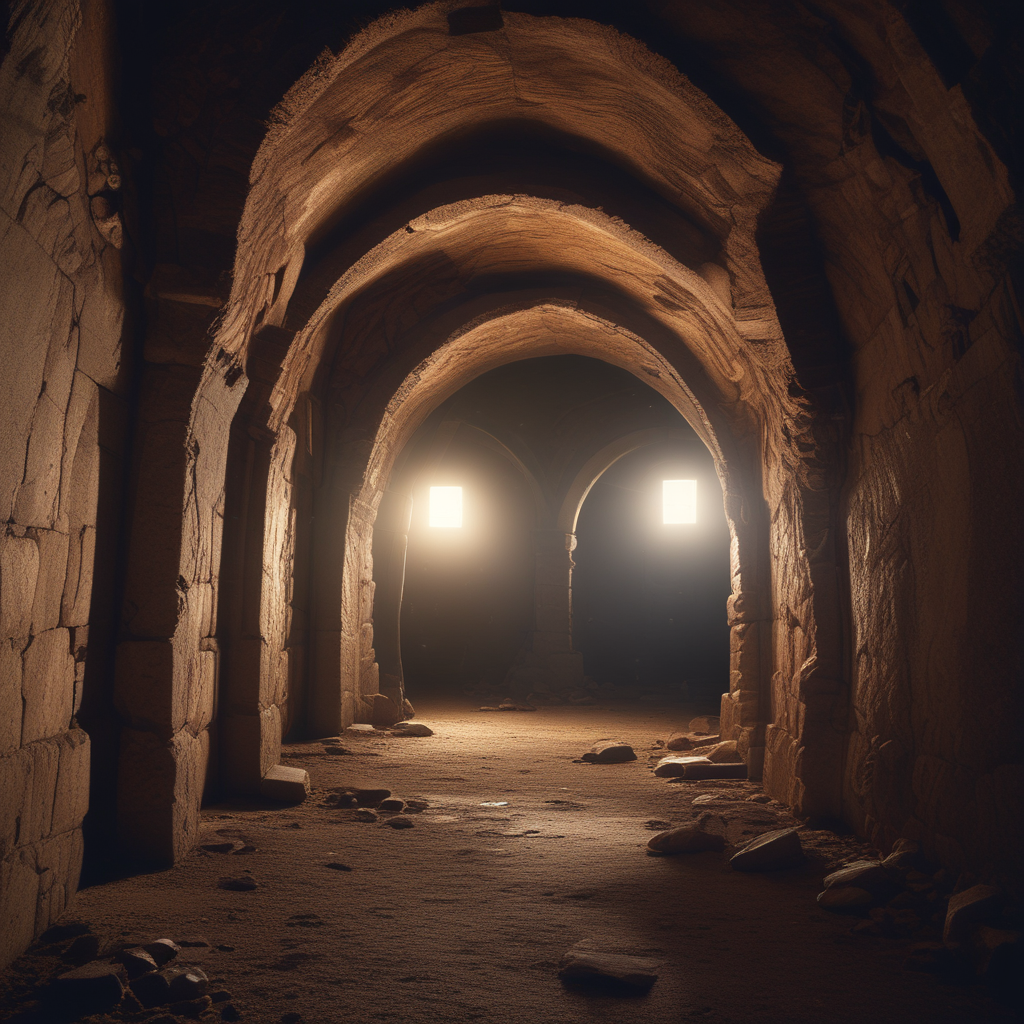

Right now, as millions of people rush through busy city streets above, an entire hidden world exists just beneath their feet. From abandoned military training facilities to forgotten subway extensions and prohibition-era smuggling routes, major cities across America sit atop vast networks of underground spaces that most residents never realize exist. Welcome to the thrilling world of urban exploration underground – where modern adventurers are rediscovering these lost pieces of urban history.
The Underground Urban Exploration Revolution
Urban exploration, commonly known as ‘urbex,’ has exploded from a niche hobby into a mainstream adventure pursuit, with millions of views on social media platforms like TikTok showcasing hidden underground gems beneath major cities. According to urbex safety experts, this underground exploration trend has become one of the most popular ways for people to seek adventure without leaving their city behind.
What makes underground tunnels cities exploration so captivating? French historian Nicolas Offenstadt explains that this enthusiasm stems from “a taste for adventure” and “a need for liberty” in increasingly organized and controlled urban environments, where such unrestricted spaces are becoming rare.
Types of Underground Spaces Waiting to Be Explored
Military Tunnels and Training Facilities
Some of the most fascinating urbex underground locations include abandoned military installations. WWI-era National Guard military training centers contain extensive underground tunnel systems that have become popular destinations for explorers. In places like Nyack, New York, abandoned military tunnels and rifle ranges showcase intricate underground networks that once served as training grounds for soldiers.
Forgotten Infrastructure Networks
Beyond military installations, cities hide various types of abandoned underground places:
- Decommissioned subway tunnels and unused station platforms
- Storm drainage systems and utility corridors
- Cold War-era fallout shelters and civil defense bunkers
- Prohibition-era smuggling routes and speakeasy tunnels
- Industrial steam tunnels and old pneumatic postal systems
Notable Underground Exploration Destinations
East Coast Underground Networks
Major East Coast cities offer some of the most extensive hidden tunnels beneath cities. New York City’s abandoned subway stations, including the famous City Hall station, represent just the tip of the iceberg. Philadelphia’s extensive utility tunnel network and Boston’s forgotten streetcar tunnels provide urban explorers with glimpses into transportation history that shaped these metropolitan areas.
West Coast Hidden Spaces
From San Francisco’s abandoned streetcar tunnels to Seattle’s underground tour areas that extend beyond the public attractions, the West Coast offers its own unique underground exploration opportunities. San Diego’s military history has left behind numerous tunnel systems, while Los Angeles harbors forgotten infrastructure from its rapid 20th-century expansion.
The Psychology Behind Underground Urban Exploration
What drives people to seek out these dark, forgotten spaces? According to research by historians specializing in urbex culture, the appeal extends far beyond mere thrill-seeking. Nicolas Offenstadt notes that urban exploration enthusiasm stems from “a passion for heritage” and serves as a form of modern archaeology.
Urban explorers often function as unofficial historians and documentarians, capturing images and stories of underground spaces before they’re permanently sealed or destroyed by development. This preservation aspect adds meaningful purpose to what might otherwise seem like simple adventure-seeking.
Freedom in Controlled Environments
As Offenstadt explains, “We live in cities that are increasingly organised and policed, in which such locations are becoming rare, and freedom of movement is extremely constricted.” Underground exploration offers a rare opportunity to experience unmonitored, unrestricted movement in urban environments where surface-level activities are heavily regulated and surveilled.
Safety, Ethics, and Legal Considerations
Responsible Exploration Practices
Safe urban exploration underground requires proper preparation and respect for legal boundaries. Experienced urban explorers emphasize several key principles:
- Research ownership and access rights before entering any underground space
- Never explore alone – always bring at least one partner
- Carry proper safety equipment including flashlights, first aid supplies, and communication devices
- Follow the “take only pictures, leave only footprints” philosophy
- Respect restricted areas and “No Trespassing” signs
Legal and Ethical Boundaries
While many underground spaces exist in legal gray areas, responsible explorers always prioritize safety and legality. Some tunnel systems are accessible through official tours or with proper permissions, while others remain strictly off-limits for safety or security reasons. The urbex community strongly emphasizes documenting and sharing these spaces responsibly without encouraging dangerous or illegal activities.
The Future of Underground Urban Exploration
As cities continue to evolve and modernize, many of these underground spaces face permanent closure or redevelopment. This makes the current era particularly significant for urban exploration enthusiasts and historians alike. Social media documentation by urban explorers serves as an invaluable record of urban infrastructure history that might otherwise be lost forever.
The growing popularity of urban exploration content on platforms like YouTube and TikTok suggests that interest in these hidden underground worlds will continue to grow, potentially leading to more organized preservation efforts and official access opportunities for historically significant sites.
The hidden world beneath our feet tells stories of urban development, military history, and infrastructure evolution that shaped the cities we know today. For those drawn to urban exploration underground, these forgotten tunnels and abandoned spaces offer a unique window into the layered history that lies just steps below the bustling surface world. As modern urban explorers continue to document and share these discoveries, they’re ensuring that these hidden chapters of city history won’t remain buried forever.
You may like

Why Your City’s Name Isn’t What You Think – The Hidden Truth Revealed


Ancient Alchemists’ Pottery Secret That Modern Science Finally Decoded


What 1 Million People Lost During 10-Hour Blackout Reveals Our Hidden Crisis


Ancient Pyramid Workers Left 4,500-Year-Old Graffiti That Rewrites History


7 Lost Cities You Can Actually Dive To – The Underwater Ruins Are Breathtaking


How Street Art Secretly Rewires Your Brain and Transforms Cities
Breaking News
Why Emergency Alerts Fail When You Need Them Most – The Truth
Emergency alerts aren’t broken—the psychology behind how we process crisis information is. Discover why officials sometimes choose NOT to send alerts during emergencies.
Published
2 days agoon
January 29, 2026
When shots rang out at Brown University, something unexpected happened: officials made the deliberate decision not to send emergency alerts. This counterintuitive choice reveals a shocking truth about emergency communications—sometimes the most dangerous thing you can do during a crisis is tell everyone about it.
The failure of emergency alert psychology isn’t about broken technology or delayed systems. It’s about the complex web of human behavior that determines whether life-saving information actually saves lives—or makes situations worse.
The Information Overload Paradox: When More News Becomes Noise
During major crises, emergency alerts face an unexpected enemy: too much information. The Emergency Alert System analysis reveals that official warnings become redundant when major events receive constant media coverage.
Consider what happened during 9/11. While Emergency Alert System messages were broadcast, they were completely overshadowed by immediate television coverage that provided more detailed, real-time information. The result? Emergency communication systems designed to be the primary source of critical information became background noise.
The Modern Media Multiplication Effect
Today’s crisis landscape is even more complex:
- Social media provides instant updates faster than official channels
- News apps send push notifications with more detail than standard alerts
- Multiple information streams create confusion about which source to trust
- Official alerts arrive after people already know about the situation
This creates a psychological phenomenon where the human brain, already overwhelmed with information, begins filtering out additional inputs—including the very emergency alerts designed to save lives.
Alert Fatigue: How Your Brain Learns to Ignore Danger
The concept of alert fatigue represents one of the most significant challenges in crisis communication psychology. When people receive frequent emergency notifications—weather warnings, AMBER alerts, test messages—their brains develop a psychological defense mechanism.
Research into emergency broadcast psychology shows that repeated exposure to non-immediately-threatening alerts creates desensitization. Each false alarm or non-critical alert reduces the likelihood that people will respond appropriately to genuinely life-threatening situations.
The Frequency Problem
Modern emergency systems face a dangerous catch-22:
- Send too few alerts: People aren’t informed about genuine risks
- Send too many alerts: People ignore critical warnings when they matter most
- Test the system regularly: Each test reduces psychological impact of real alerts
- Don’t test enough: Technical failures occur during actual emergencies
The psychological impact compounds over time, creating communities that are technically well-informed but behaviorally unresponsive to crisis alert effectiveness.
The Strategic Psychology of When NOT to Alert
The Providence Journal’s reporting on the Brown University shooting reveals a sophisticated understanding of emergency psychology that goes beyond simple “warn everyone” strategies.
Providence officials deliberately chose not to send statewide emergency alerts during the active shooting situation due to safety concerns about alerting the perpetrator. This decision represents a evolution in emergency alert psychology—understanding that information distribution can sometimes endanger the very people it’s meant to protect.
Unintended Psychological Consequences
Emergency management experts now recognize several scenarios where alerts can backfire:
- Alerting perpetrators to law enforcement knowledge and response
- Creating panic-driven behaviors that increase danger (stampedes, dangerous driving)
- Overwhelming emergency services with unnecessary calls from panicked citizens
- Interfering with tactical operations that require secrecy or surprise
This strategic approach to emergency communications represents a fundamental shift from broadcast-everything policies to psychologically-informed crisis management.
The Evolution to Interactive Emergency Psychology
Modern emergency systems are evolving beyond one-way information broadcasting toward two-way communication systems that leverage crowd psychology for enhanced crisis response.
The Douglas County DougCoAlert system represents this new approach, allowing residents to answer poll questions that provide officials with critical real-time information during emergency situations.
Psychological Benefits of Interactive Systems
Two-way emergency communication addresses several psychological factors that undermine traditional alerts:
- Engagement over passivity: Active participation increases psychological investment
- Personalized information: Targeted messages feel more relevant and urgent
- Feedback loops: Citizens feel heard and officials get better situational awareness
- Community connection: Shared response creates psychological solidarity
This interactive approach transforms emergency management from information distribution to collaborative crisis response, working with human psychology rather than against it.
Beyond Technology: The Future of Crisis Communication Psychology
The National Emergency Message system was designed as a “last-ditch effort to get a message out if the president cannot get to the media.” This definition reveals the fundamental assumption behind emergency alerts: that information distribution equals effective communication.
However, understanding emergency alert psychology shows that effective crisis communication requires much more sophisticated approaches:
- Behavioral prediction models that anticipate how different populations will respond to specific alert types
- Psychological timing strategies that optimize when and how information is delivered
- Cultural communication adaptation that accounts for diverse community response patterns
- Trauma-informed messaging that minimizes psychological harm while maximizing safety compliance
The Integration Challenge
Future emergency systems must balance multiple psychological factors simultaneously: urgency without panic, completeness without overload, authority without alienation, and speed without inaccuracy.
The most effective crisis alert effectiveness will come from systems that understand human psychology as deeply as they understand technology, creating communication strategies that work with natural human responses rather than expecting people to override their psychological instincts during high-stress situations.
The failure of emergency alerts isn’t a technical problem—it’s a human one. By recognizing the complex psychology behind how we process crisis information, emergency management can evolve from systems that broadcast information to systems that truly communicate, building trust and saving lives through psychological understanding rather than technological force.
Global News
304 Million People Send $800 Billion Home – The Hidden Economy Reshaping Nations
Discover how 304 million global migrants create an $800 billion invisible economy through remittances, surpassing foreign aid and transforming entire countries.
Published
2 weeks agoon
January 19, 2026
Right now, as you read this, 304 million people living outside their birth countries are quietly powering one of the world’s largest financial networks. They’re not bankers, CEOs, or government officials – they’re migrant workers sending money home, creating an $800 billion annual economy that dwarfs most national budgets and exceeds all official foreign aid combined.
The Staggering Scale of Global Remittances Migration
The numbers behind global remittances migration tell a story that most people never hear about. According to the Visual Capitalist’s global migration analysis, we’re witnessing the highest levels of international migration in human history. But it’s not just about movement – it’s about the invisible financial highways these migrants create.
Every year, these 304 million migrants collectively send home more money than the GDP of most countries. To put this in perspective:
- $800+ billion flows through remittance channels annually
- This exceeds the total foreign aid budgets of all developed nations combined
- Some countries receive remittances worth 20-30% of their entire GDP
- The average migrant sends home $2,600 per year
Why One Country Dominates the Global Migration Map
Here’s where the story gets fascinating: the United States hosts more migrants than the next four destination countries combined. This isn’t just about opportunity – it’s about creating the world’s largest remittance-sending hub.
The Concentration Effect
While migrants come from every corner of the globe, they don’t spread evenly. The top destination countries create what economists call “remittance powerhouses”:
- United States – Over 50 million migrants
- Germany – 15.8 million migrants
- Saudi Arabia – 13.5 million migrants
- Russia – 11.6 million migrants
- United Kingdom – 9.4 million migrants
This concentration means that economic policies in just a handful of countries can impact the financial lifelines of hundreds of millions of families worldwide.
The Money Trail That Beats Foreign Aid
Perhaps the most mind-blowing aspect of global remittances migration is how these personal transfers have become more significant than official government aid programs. The World Bank’s Migration and Remittances data reveals that migrant workers are essentially running the world’s largest private foreign aid program.
Where the Money Flows
The top remittance-receiving countries showcase how international money transfer patterns reshape entire economies:
- India – Receives over $100 billion annually
- China – Over $50 billion in remittances
- Mexico – Approximately $60 billion yearly
- Philippines – Around $35 billion annually
- Pakistan – Nearly $30 billion in remittances
These aren’t just numbers – they represent millions of families paying for education, healthcare, housing, and starting small businesses that drive local economic growth.
Two Migration Stories: Economic Dreams vs. Crisis Survival
Understanding global migration patterns requires recognizing that not all migration is the same, and neither are the resulting remittance flows.
Economic Migration: The Planned Journey
Countries like India and China lead in economic migration, with workers strategically moving to higher-wage countries. These migrants often:
- Send steady, predictable amounts home monthly
- Support long-term family investments like education and property
- Create lasting financial connections between regions
- Build networks that facilitate future migration
Crisis-Driven Displacement: Survival Mode
Meanwhile, crisis-driven migration from countries like Ukraine, Syria, and Venezuela creates different remittance patterns. According to UNHCR displacement statistics, these migrants typically:
- Send irregular amounts based on immediate family needs
- Focus on emergency support rather than investment
- Face greater challenges accessing traditional banking services
- Rely more heavily on digital and informal transfer methods
The Digital Revolution Transforming Money Movement
Technology is revolutionizing how migrant workers send money home, making the $800 billion remittance economy more efficient than ever before. Traditional bank transfers that once took days and cost 8-12% in fees are being replaced by digital solutions charging 2-3% with instant delivery.
The New Digital Landscape
Modern remittance technology includes:
- Mobile money platforms enabling phone-to-phone transfers
- Blockchain-based services reducing costs and increasing speed
- Digital wallets that work across borders seamlessly
- Cryptocurrency options for tech-savvy users in certain corridors
This digital transformation means more money reaches families instead of being lost to fees, amplifying the economic impact of every dollar sent.
Beyond Numbers: The Human Impact of Global Remittances
While the scale of global remittances migration is impressive, the real story lies in how these transfers transform lives and communities. IFAD research on remittances shows that families receiving money from abroad are:
- 40% more likely to send children to school
- 60% more likely to start a small business
- 35% less likely to live in extreme poverty
- More resilient during economic downturns and natural disasters
The Multiplier Effect
Every dollar sent home doesn’t just help one family – it circulates through local economies. When migrants send money home, recipients typically spend 85% locally on:
- Food and basic necessities
- Education and healthcare
- Housing improvements
- Small business investments
- Community projects and local services
The Future of the $800 Billion Migration Economy
As we look ahead, several trends will shape the future of global remittances migration. Climate change is expected to drive new migration patterns, potentially creating additional remittance corridors. Meanwhile, artificial intelligence and blockchain technology promise to make transfers even cheaper and faster.
The 304 million migrants currently sending money home represent just the beginning. As global connectivity increases and economic opportunities remain unevenly distributed, this invisible financial network will likely grow even larger, continuing to reshape economies and support families across the globe.
What started as individual decisions to seek better opportunities abroad has evolved into one of the most significant financial forces in the modern world – a testament to human connection and the power of shared prosperity across borders.
Global Issues
Why Internet Access Transforms Poverty Into Revolution Changes Everything
The shocking connection between internet access inequality and global civil unrest – how digital connectivity turns silent suffering into organized resistance movements worldwide.
Published
2 weeks agoon
January 19, 2026
In 2024, a protestor in Santiago livestreamed the moment they stood outside a tech billionaire’s mansion while unable to afford basic internet at home. This single image – shared millions of times – perfectly captured the explosive collision between digital access and wealth disparity that’s reshaping global society. What researchers are discovering about internet access inequality will fundamentally change how we understand modern revolutions.
The Staggering Numbers Behind Global Wealth Concentration
The latest World Inequality Report 2026 reveals a shocking reality: the richest 10% of the global population now owns 75% of all wealth and receives 53% of all income. Meanwhile, according to the 2024 Oxfam report, roughly five billion people have become poorer while the five richest individuals have doubled their fortunes.
These aren’t just abstract statistics – they represent the most extreme concentration of resources in human history. In the United States alone, the Gini index rose by 1.2% in 2021 to 0.494, indicating growing inequality even as many other countries saw declining disparities during COVID-19.
The Human Cost of Extreme Inequality
- Income disparity: Global inequality spans income, wealth, gender, and climate dimensions
- Urban poverty: Too many urban residents face extreme poverty despite living in centers of wealth
- Volatile family incomes: Economic instability increases social tensions and populist criticism
- Democratic threats: Extreme inequality threatens the fabric of democratic institutions
The Digital Catalyst: How Internet Access Transforms Silent Suffering
Here’s where the story takes a revolutionary turn. Research on global protest patterns reveals that internet access acts as the crucial spark that transforms inequality into civil unrest. Before widespread connectivity, vast populations could experience severe inequality without means to coordinate responses or fully understand the scope of disparity.
The digital revolution has created what experts call the ‘information inequality nexus’ – where access to information about wealth gaps, combined with tools for organization and communication, turns economic frustration into social movements.
The Visibility Paradox
Internet access creates a psychological tension that didn’t exist in pre-digital societies. People become simultaneously more aware of global wealth and more frustrated with their local conditions. Social media platforms now allow individuals to witness extreme wealth displays – luxury lifestyles, private jets, mega-yachts – while struggling with basic needs, creating instant emotional triggers for social unrest.
Real-Time Revolution: How Digital Tools Accelerate Social Movements
The speed of modern revolutions has fundamentally changed. Digital organizing tools can transform economic grievances into mass movements within days rather than years. Recent global protests demonstrate how hashtags become rallying cries faster than traditional media can respond.
Case Studies in Digital-Driven Unrest
From the Arab Spring to recent protests across developing nations, we’re witnessing unprecedented levels of civil unrest worldwide. The common thread isn’t just economic inequality – it’s the combination of inequality with internet connectivity that enables:
- Rapid organization: Protest coordination through messaging apps and social media
- Real-time documentation: Livestreaming of wealth disparity and police responses
- Global solidarity: International awareness and support for local movements
- Information sharing: Tactics, strategies, and inspiration spreading across borders
The Psychology of Connected Inequality
Understanding why internet access creates revolutionary conditions requires examining the psychological impact of digital connectivity on inequality awareness. When people can see wealth concentration in real-time while experiencing poverty, it creates what researchers call relative deprivation on steroids.
Before the internet, economic inequality existed in isolated pockets. A poor farmer in rural Bangladesh might never know about Silicon Valley tech fortunes. Today, global wealth displays are just a click away, making local poverty feel more acute and unjust.
The Emotional Triggers of Digital Inequality
- Instant comparison: Real-time wealth displays versus personal financial struggles
- Access barriers: Seeing opportunities online while lacking resources to participate
- Information gaps: Understanding global systems while feeling powerless locally
- Community formation: Finding others with similar grievances and frustrations
Expert Solutions: Bridging Both Digital and Wealth Divides
Nobel Prize winner Joseph E. Stiglitz offers hope: “Progressive taxation, strong social investment, fair labor standards, and democratic institutions have narrowed gaps in the past—and can do so again.” The key insight is that extreme inequality isn’t inevitable.
Economic research by Thomas Piketty and Martin Wolf confirms that addressing both inequality and internet access requires coordinated policy responses:
Comprehensive Solutions
- Digital infrastructure investment: Ensuring universal internet access as a basic right
- Progressive taxation: Redistributing wealth concentration more effectively
- Education and digital literacy: Empowering people to use connectivity constructively
- Transparent governance: Using digital tools to increase democratic participation
- Economic opportunity creation: Leveraging internet access for income generation
The evidence is clear that both digital divides and wealth gaps must be addressed simultaneously to prevent larger conflicts.
Future Implications: Navigating the Connected Inequality Era
As internet access continues expanding globally, the relationship between connectivity and inequality will only intensify. The question isn’t whether digital access will continue transforming economic frustration into social movements – it’s whether societies will proactively address these challenges or reactively manage the consequences.
The hidden connection between internet access inequality and social unrest represents one of the most significant drivers of modern political instability. Understanding this relationship is crucial for anyone seeking to comprehend why our world seems increasingly volatile and how we might build more equitable, stable societies.
The livestream from Santiago wasn’t just a moment of protest – it was a preview of our connected, unequal future. The question now is what we’ll do with this knowledge before the next revolution goes viral.

Why Emergency Alerts Fail When You Need Them Most – The Truth

Why Your City’s Name Isn’t What You Think – The Hidden Truth Revealed

Ancient Persia’s Secret Weapon That Built History’s First Superpower

Hidden Economic Warfare: How Climate Deals Secretly Control Global Trade

7 Anonymous Heroes Who Changed History Forever – 3 Will Shock You

Scientists Just Discovered What Renaissance Artists Knew All Along – It Changes Everything
Trending

 Global News1 month ago
Global News1 month agoHidden Economic Warfare: How Climate Deals Secretly Control Global Trade

 Historical Figures2 months ago
Historical Figures2 months ago7 Anonymous Heroes Who Changed History Forever – 3 Will Shock You
 Art & Design2 months ago
Art & Design2 months agoScientists Just Discovered What Renaissance Artists Knew All Along – It Changes Everything

 Fun Facts2 months ago
Fun Facts2 months agoScientists Just Discovered Space Isn’t Silent – The Sounds Will Shock You
 Global News3 months ago
Global News3 months agoUndefined Behavior Programming: The Hidden Digital Threat

 News & World2 months ago
News & World2 months agoUrban Explorers’ Most Terrifying Encounters in ‘Empty’ Buildings

 Lifestyle & Culture2 months ago
Lifestyle & Culture2 months agoScientists Just Discovered What 1-Minute Workouts Do to Your Body (Mind-Blowing Results)

 News & World2 months ago
News & World2 months ago7 Bizarre Travel Destinations That Defy All Logic (Scientists Are Baffled)

